News
Precision Machining Processes: A Comprehensive Overview
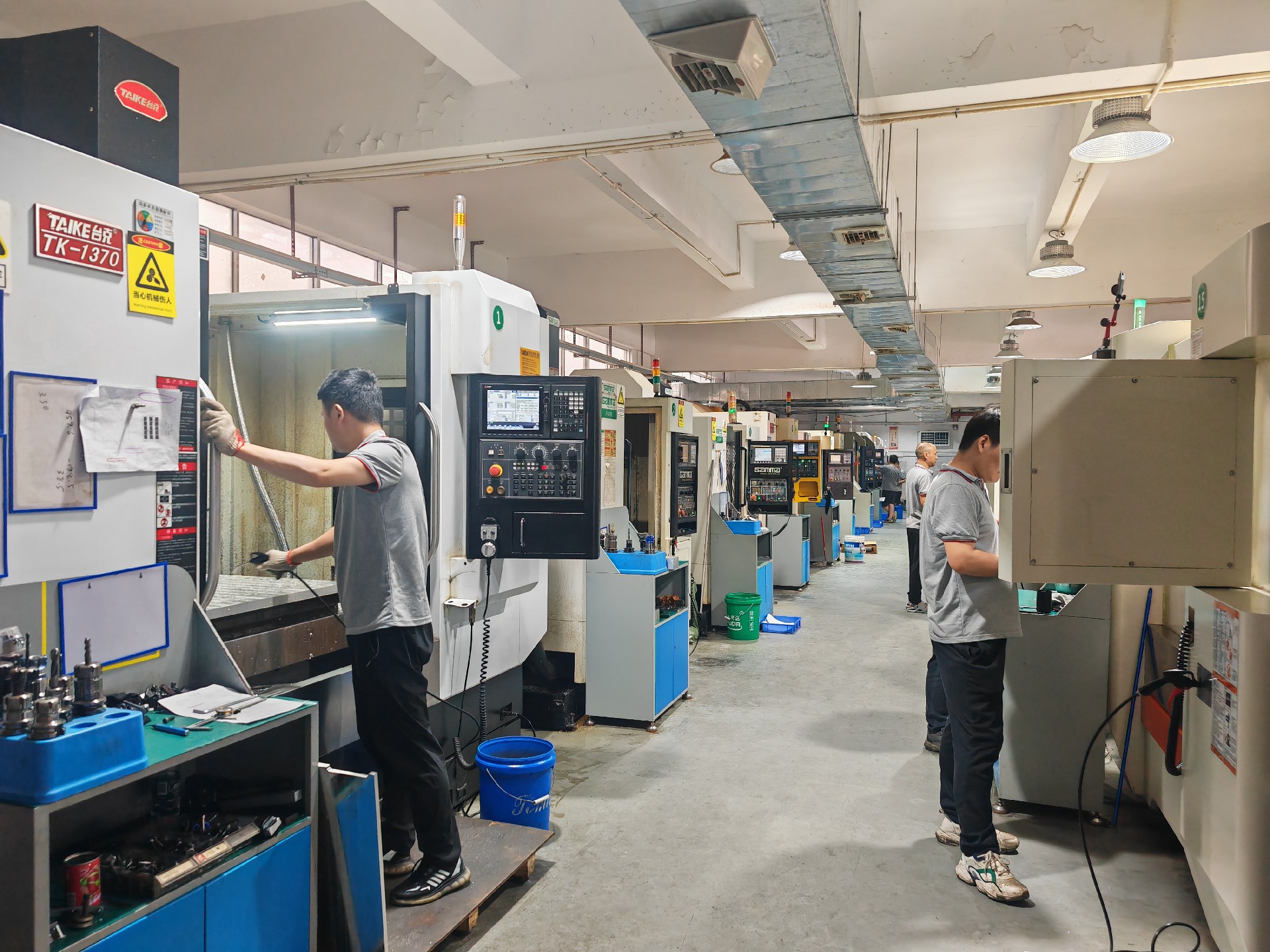
Precision machining is the backbone of high-quality manufacturing, producing parts with extremely tight tolerances (as fine as ±0.001") and superior surface finishes. Industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive rely on these processes to create complex, high-performance components.
Here are the key precision machining processes used in modern manufacturing:
1. CNC Milling
Uses multi-axis CNC machines (3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis) to remove material from a workpiece.
Ideal for complex geometries, pockets, slots, and contours.
Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants, automotive parts.
2. CNC Turning
A lathe rotates the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it.
Best for cylindrical parts (shafts, bushings, couplings).
Can be combined with live tooling for milling operations in CNC turning centers.
3. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
Uses electrical sparks to shape hard metals like titanium and tungsten.
Two types:
Wire EDM – Cuts intricate shapes with a fine wire (e.g., turbine blades).
Sinker EDM – Shapes molds and dies with high precision.
4. Grinding
Achieves ultra-fine tolerances (±0.0001") through abrasive removal.
Types: Surface, cylindrical, and centerless grinding.
Used in ball bearing races, optical lenses, and precision gears.
5. Laser & Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting – High-accuracy cutting for metals and plastics (no tool wear).
Waterjet cutting – Cold-cutting process for heat-sensitive materials.
6. Micro-Machining
Manufactures tiny components (< 1mm) for electronics & medical devices.
Uses high-speed CNC machines and ultra-fine tooling.
Which Process is Right for Your Project?
The choice depends on material, tolerances, complexity, and volume. RenJie specializes in high-precision machining—delivering quality, speed, and cost-efficiency.

- Previous:What is precision machining
- Next:没有了!